
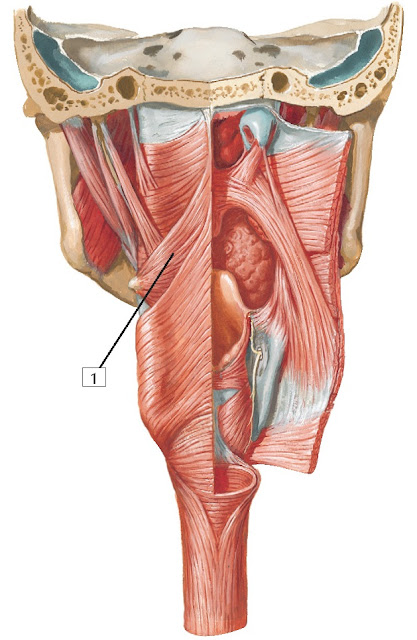
from the basilar part of the occipital bone and the adjacent temporal bone. The pharyngobasilar fascia (the deep investing/epimysial layer of the external pharyngeal mm.) suspends the superior pharyngeal constrictor m. Rami pharyngei – motorically innervates the upper sphincter of the pharynx, the sensitive mucous membrane, and the parasympathetic nerve innervates small glands in the mucous membrane.Note: The pharynx is supported by two associated bodies of fascia: pharyngobasilar fascia and buccopharyngeal fascia.Ramus musculi stylopharyngei - motorically innervates the stylopharyngeus muscle.Ramus communicans cum ramo auriculari nervi vagi.Postganglionic fibers continue to the parotid gland via the mandibular nerve. tympanicus, after receiving the sympathetic and motor components, goes to the otic ganglion already as lesser petrosal nerve. The parasympathetics continue from the tympanic plexus to the minor petrous nerve and through it to the otic ganglion and then passes through the ramus communicans cum nervo auriculotemporalis to the auriculotemporal nerve from the trigeminal nerve V3 and through it finally to the parotid gland. tympanicus conducts sensory fibers to innervate the mucosa of the middle ear cavity and the wall of the auditory tube. Nervus tympanicus – separates at the level of the ganglion inferius and passes upwards through the canaliculus tympanicus into the middle ear cavity to the promontory, forming the plexus tympanicus, into which several other connections go ( Jacobson's anastomosis).It reaches the radix linguae and the deep part of the styloglossus muscle and sinks into the tongue. It runs parallel to the stylopharyngeus muscle' below and expands, joining the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle. It is located under the base of the skull behind the internal carotid artery, below it runs between the internal carotid artery and the internal jugular vein. It emerges from the oblongata, continues to the common exit from the skull through the jugular foramen, where it has the superior and inferior ganglion of the vagus nerve. Spinal nucleus of the trigeminal nerve - viscerosensitive and somatosensitive fibres from the palate, middle ear, palatine tonsil nucleus of tractus solitarius – viscerosensitive fibres from the dorsal third of the tongue.Inferior Salivatory Nucleus – parasympathetic visceromotor for parotid gland.It provides sensory innervaton the posterior third of the tongue for the sensation of taste.It provides sensory innervation to the middle ear cavity, auditory tube, pharynx, tonsils, and the back third of the tongue.It parasympathetically innervates the mucosa of the middle ear cavity and the otic ganglion.The exception is the tensor veli palatini muscle, which innervates the C.N. It motorically innervates the muscles of the palate, pharynx and stylopharyngeus muscle.All these nerves exit the brainstem laterally from the olive in the posterolateral sulcus and contain all types of fibers. Together with the vagus nerve and the accessory nerve, it belongs to the lateral mixed system. It also has a sensory function, as it guides taste sensations.

It is a mixed nerve with a motor, sensitive and parasympathetic component. Template:Infobox - nerv The glossopharyngeal nerve is the ninth cranial nerve.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
